Workshop Secrets: 12 tips on common defects and preventive measures of aluminum and aluminum alloy welding

Generally, welding wires with the same or similar brand as the base metal are used for welding aluminum and aluminum alloy, so as to obtain better corrosion resistance; However, when welding heat treatment strengthening aluminum alloy with large tendency of hot cracking, the selection of welding wire mainly starts from solving the crack resistance. At this time, the composition of welding wire is very different from that of base metal.
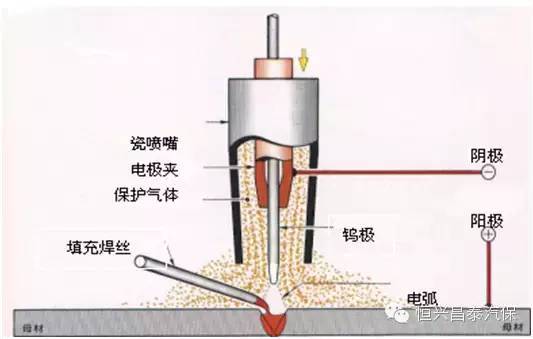
Common defects (welding problems) and preventive measures
1. Burn through
Causes:
a. Excessive heat input;
b. Improper groove processing and excessive assembly clearance of weldments;
c. When spot welding, the spacing between welding points is too large, resulting in large deformation in the welding process.
Preventive measures:
a. Properly reduce the welding current and arc voltage and improve the welding speed;
b. Large blunt edge size to reduce root clearance;
c. Properly reduce the welding spot spacing during spot welding.
2. Stomata
Causes:
a. There is oil, rust, dirt, scale, etc. on the base metal or welding wire;
b. The air flow in the welding site is large, which is not conducive to gas protection;
c. The welding arc is too long to reduce the effect of gas protection;
d. The distance between the nozzle and the workpiece is too large, and the gas protection effect is reduced;
e. Improper selection of welding parameters;
f. Air holes are generated at repeated arcing;
g. The purity of shielding gas is low and the effect of gas protection is poor;
h. The ambient air humidity is high.
Preventive measures:
a. Carefully clean the oil, dirt, rust, scale and oxide film on the surface of welding wire and weldment before welding, and use the welding wire with high deoxidizer;
b. Reasonable selection of welding sites;
c. Properly reduce the arc length;
d. Maintain a reasonable distance between the nozzle and the weldment;
e. Try to choose thicker welding wire and increase the thickness of the blunt edge of the workpiece groove. On the one hand, large current can be allowed, on the other hand, the proportion of welding wire in the weld metal can be reduced, which is effective to reduce the porosity;
f. Try not to repeat arcing at the same part. If it is necessary to repeat arcing, polish or scrape off the arcing part; Once a weld is arced, it shall be welded as long as possible, and do not break the arc at will, so as to reduce the amount of joints. There shall be a certain weld overlap area at the joint;
g. Change protective gas;
h. Check the air flow;

3. Arc instability
Causes:
Power cord connection, dirt or wind.
Preventive measures:
a. Check all conductive parts and keep the surface clean;
b. Remove the dirt at the joint;
c. Try not to weld in places that can cause turbulence of air flow.
4. Poor weld formation
Causes:
a. Improper selection of welding specifications;
b. Incorrect welding gun angle;
c. The welder is not skilled;
d. The hole diameter of the conductive nozzle is too large;
e. Welding wire, weldment and shielding gas contain moisture.
Preventive measures:
a. Repeated commissioning and selection of appropriate welding specifications;
b. Maintain proper inclination angle of welding gun;
c. Select the appropriate diameter of the conducting nozzle;
d. Carefully clean the welding wire and weldment before welding to ensure the purity of gas.
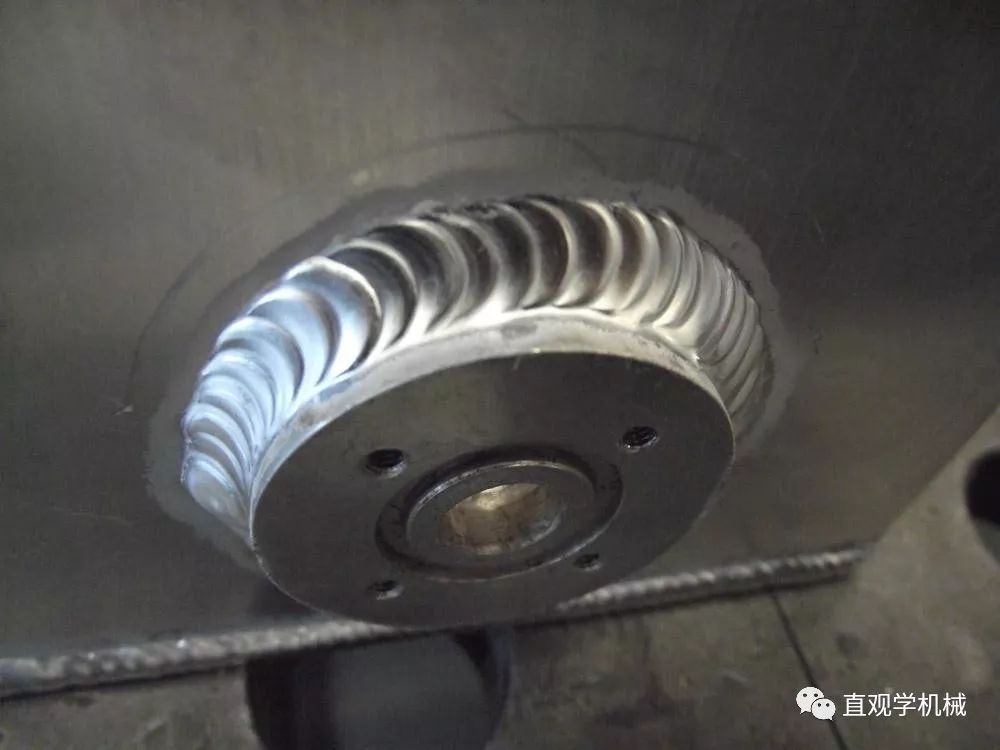
5. Incomplete penetration
Causes:
a. The welding speed is too fast and the arc is too long;
b. Improper groove processing and too small equipment clearance;
c. The welding specification is too small;
d. The welding current is unstable.
Preventive measures:
a. Lower the welding speed properly and slow down the welding arc;
b. Properly reduce the blunt edge or increase the root gap;
c. Increase welding current and arc voltage to ensure sufficient heat input energy of base metal;
d. Add regulated power supply device
e. Fine welding wire is helpful to improve the penetration, and coarse welding wire can improve the deposition amount, which should be selected as appropriate.

6. Incomplete fusion
Causes:
a. The oxide film or rust on the welding part is not removed completely;
b. Insufficient heat input.
Preventive measures:
a. Clean the surface of the place to be welded before welding
b. Increase welding current and arc voltage and reduce welding speed;
c. For thick plates, U-joints are used, but V-joints are generally not used.
7. Crack
Causes:
a. The structural design is unreasonable and the weld is too concentrated, resulting in excessive restraint stress of the welded joint;
b. The molten pool is too large, overheated, and the alloy elements are burned too much;
c. The crater at the end of the weld cools quickly;
d. The composition of welding wire does not match the base metal;
e. The weld depth width ratio is too large.
Preventive measures:
a. Correctly design the welding structure, reasonably arrange the welds, avoid the stress concentration area as far as possible, and reasonably select the welding sequence;
b. Reduce the welding current or appropriately increase the welding speed;
c. The arc stopping operation shall be correct, and the arc striking plate shall be added or the current attenuation device shall be used to fill the arc pit;
d. Select welding wire correctly.
8. Slag inclusion
Causes:
a. Incomplete cleaning before welding;
b. Excessive welding current leads to partial melting of the conductive nozzle and mixing into the molten pool to form slag inclusion;
c. Welding speed is too fast.
Preventive measures:
a. Strengthen the cleaning before welding. In case of multi pass welding, the weld shall be cleaned after each pass of welding;
b. Under the condition of ensuring penetration, the welding current shall be appropriately reduced, and the conductive nozzle shall not be pressed too low during high current welding;
c. Appropriately reduce the welding speed, use the welding wire with high deoxidizer and increase the arc voltage.
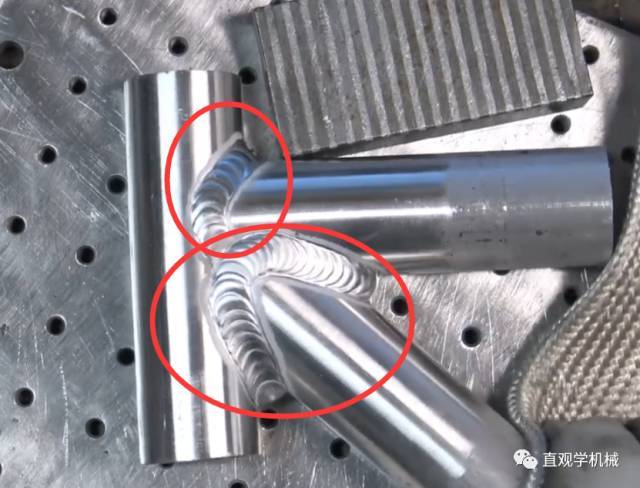
9. Undercut
Causes:
a. The welding current is too large and the welding voltage is too high;
b. Too fast welding speed and too little wire filling;
c. The welding gun swings unevenly.
Preventive measures:
a. Adjust welding current and arc voltage properly;
b. Appropriately increase the wire feeding speed or reduce the welding speed;
c. The welding gun shall swing evenly.

10. Weld contamination
Causes:
a. Improper shielding gas coverage;
b. Dirty welding wire;
c. The base metal is dirty.
Preventive measures:
a. Check whether the air supply hose has leakage, whether there is air extraction, whether the air nozzle is loose, and whether the protective gas is used correctly;
b. Whether welding materials are stored correctly;
c. Remove oil and grease before using other mechanical cleaning;
d. Remove the oxide before using the stainless steel brush.
11. Poor wire feeding
Causes:
A. Ignition between conductive nozzle and welding wire;
b. Wear of welding wire;
c. Arc spraying;
d. The wire feeding hose is too long or too tight;
e. Improper or worn wire feeding wheel;
f. There are many burrs, scratches, dust and dirt on the surface of welding materials.
Preventive measures:
a. Reduce the tension of wire feeding wheel and use slow start system;
b. Check the contact surface of all welding wires and minimize the contact surface between metal and metal;
c. Check the condition of conductive nozzle and wire feeding hose, and check the condition of wire feeding wheel;
d. Check whether the diameter and size of the conductive nozzle match;
e. Use wear-resistant materials to avoid cutting off during wire feeding;
f. Check the wear condition of welding wire disc;
g. Select the appropriate size, shape and surface condition of the wire feeding wheel;
h. Select welding materials with good surface quality.
12. Poor arcing
Causes:
a. Poor grounding;
b. The size of the conductive nozzle is incorrect;
c. No shielding gas.
d. Change welding parameters.

